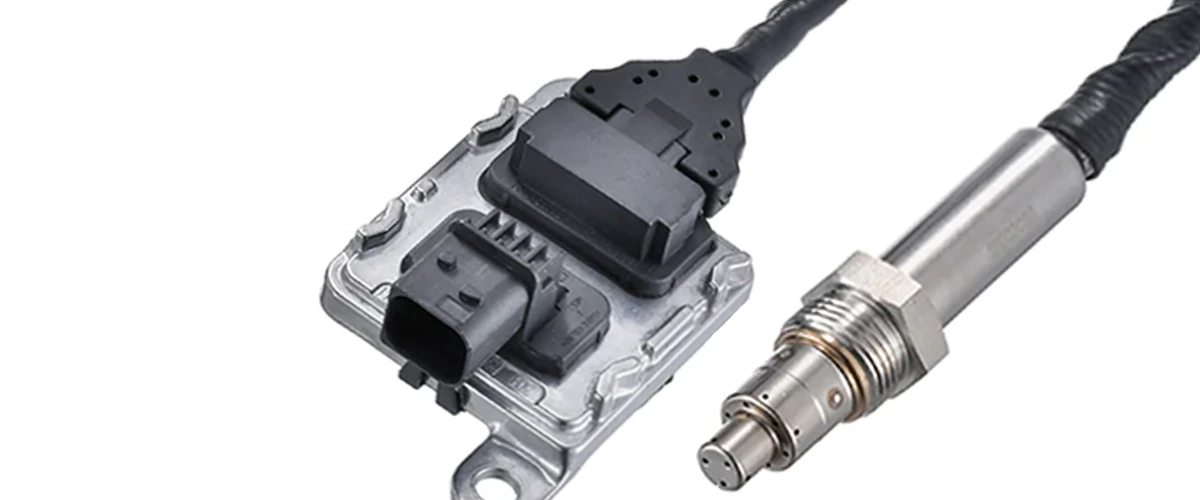
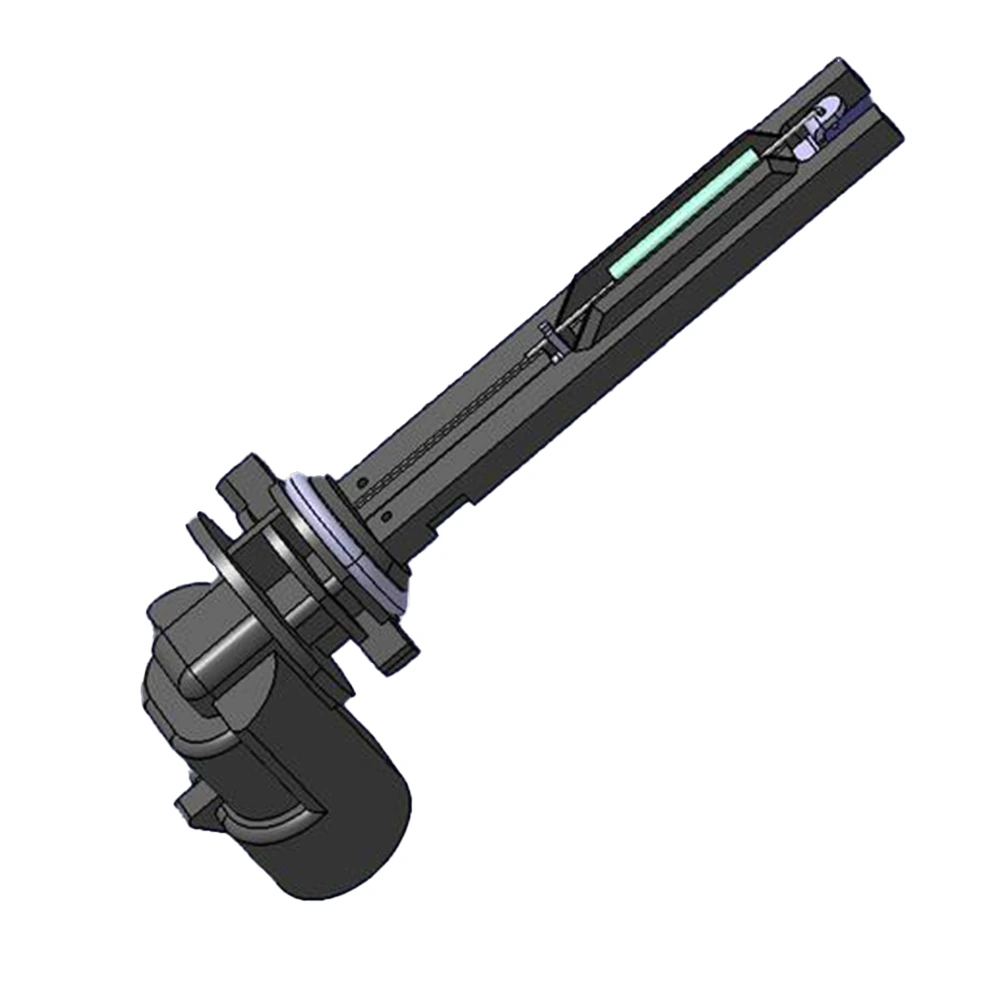
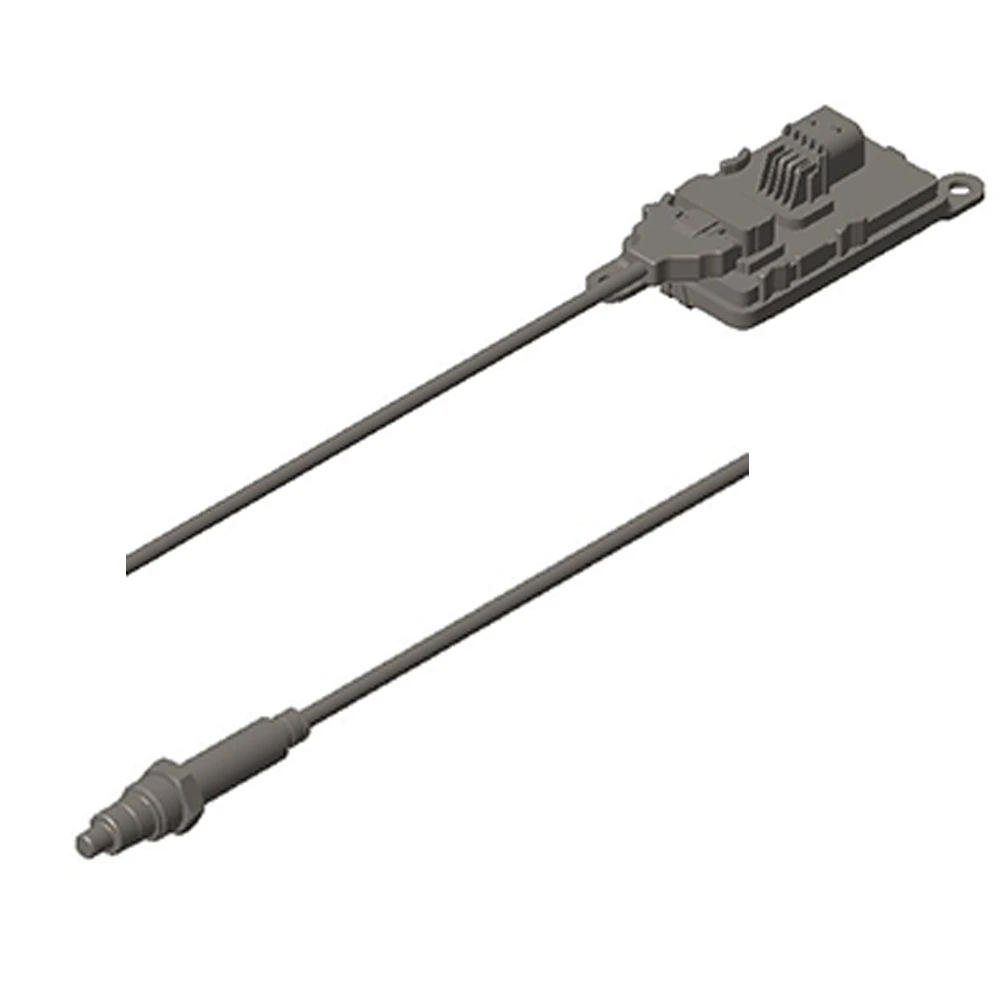
Particulate Matter (PM) sensors are critical for monitoring soot levels and triggering DPF regeneration. When a sensor fault occurs, inaccurate readings can lead to failed regeneration, increased emissions, or even engine derating. Early diagnosis of fault codes helps maintain compliance and prevents costly downtime.
1. Overview of OBD-II and DTCs
Onboard diagnostics (OBD-II) standardizes fault codes for emission-related components. Generic codes (P24xxx) cover PM sensor circuits, while OEMs may define additional manufacturer-specific codes. Accessing these codes via a scan tool is the first step in troubleshooting.
2. Top 5 Common PM Sensor Fault Codes
- P24AF: Particulate Matter Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Indicates the sensor output is outside expected range during self-test.
- P24A5: PM Sensor Circuit Low Voltage or current reading below minimum threshold—possible wiring short or sensor contamination.
- P24A6: PM Sensor Circuit High Signal above maximum threshold—could result from open circuit, corroded connector, or excessive soot buildup.
- P24A7: PM Sensor Not Detected No communication with sensor—likely due to wiring fault or failed sensor element.
- Manufacturer-Specific Code (e.g., P2210) Some OEMs use custom codes to indicate calibration errors or drift beyond compensation limits.
3. Root Causes and Troubleshooting
For each code, follow these steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check sensor harness, connectors, and mounting for damage or corrosion.
- Circuit Test: Measure voltage/current at the sensor connector against specifications.
- Cleaning: If optical sensor, remove and gently clean lens with isopropyl alcohol. For resistive, perform active regeneration cycles.
- Sensor Bench Test: Use a diagnostic tester to simulate exhaust conditions and verify sensor response.
- Replace if Necessary: If readings remain out of range after repair, install new sensor.
4. Preventive Maintenance Best Practices
- Schedule regular DPF inspections and cleanings
- Use high-quality, low-sulfur diesel to reduce contamination
- Ensure proper grounding and shielded wiring installations
- Update ECU and sensor firmware for improved self-test algorithms
5. When to Seek Professional Assistance
If fault codes persist after basic troubleshooting or if complex OEM-specific codes appear, consult certified technicians. Professional diagnostic equipment and factory calibration procedures ensure accurate repair and restore reliable PM sensing.
Understanding and resolving PM sensor fault codes quickly is essential for emission compliance and vehicle uptime. By following systematic diagnostic steps and preventive maintenance practices, technicians can minimize faults, optimize DPF performance, and avoid costly repairs.