As global emission regulations tighten, reducing particulate emissions has become a top priority for both governments and manufacturers. Among the technologies enabling this change, the Particulate Matter (PM) sensor plays a critical role. This article explains what a PM sensor is, how it works, and why it is indispensable for modern emission systems.
What is a PM Sensor?
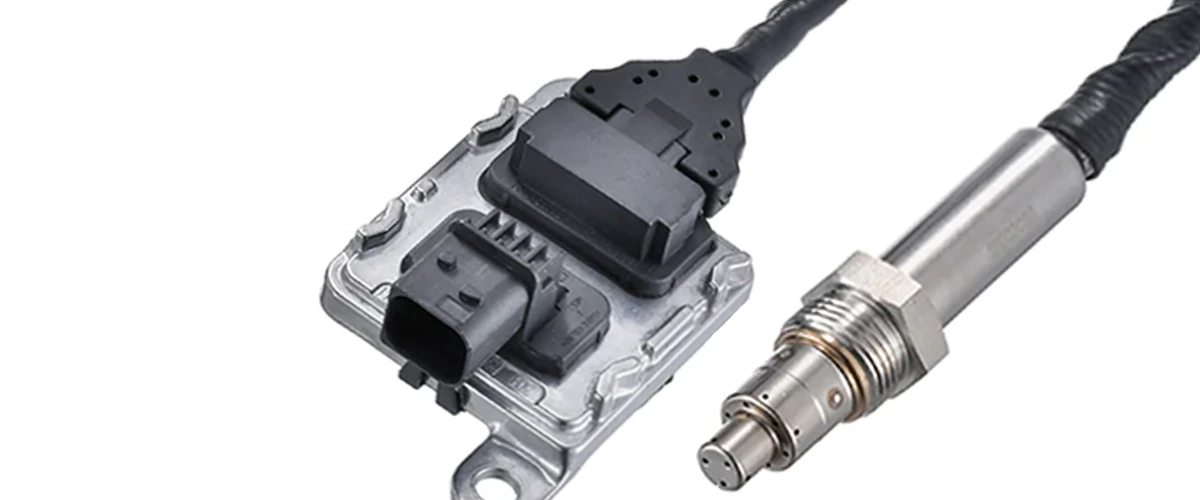
A PM sensor is an exhaust gas sensor designed to detect and quantify the amount of particulate matter (PM)—specifically soot particles—emitted from internal combustion engines. These particles are primarily composed of unburned hydrocarbons, metals, and other compounds that pose significant health and environmental risks.
Why PM Sensors Matter
PM sensors help ensure compliance with emissions regulations such as Euro 6/7, EPA 13, and China 6 by monitoring the performance of Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs). Without these sensors, vehicles would not be able to:
- Determine the exact soot load in the exhaust system
- Trigger DPF regeneration events efficiently
- Detect failures or clogging in the DPF system
- Report real-time emission data to Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) systems
Key Benefits of PM Sensors
- Regulatory Compliance: Keeps emissions below legal limits.
- Engine Efficiency: Ensures optimal engine backpressure by prompting timely filter regeneration.
- Cost Savings: Prevents excessive fuel consumption and unplanned maintenance.
- Health & Environment: Reduces the release of harmful particulates into the atmosphere.
Types of PM Sensors
There are various PM sensing technologies, including:
- Resistive Soot Sensors: Measure the conductivity change as soot accumulates between electrodes.
- Optical PM Sensors: Use light scattering to detect the presence and density of particles.
- Capacitive Sensors: Monitor changes in dielectric properties due to particle deposition.
Applications
PM sensors are widely used in:
- Passenger cars with diesel engines
- Heavy-duty trucks and buses
- Construction and agricultural machinery
- Hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles
In the age of stricter emissions control and environmental responsibility, PM sensors are more important than ever. By accurately detecting particulate matter levels, these sensors enable smarter, cleaner, and more efficient engines. As a key part of your emission system, choosing the right PM sensor is critical to maintaining performance and compliance.